Online calculator to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (°C to °F) with formulas, examples, and tables. Our conversions provide a quick and easy way to convert between Temperature units.
- Temperature Conversion Table
- Temperature Conversion Equation
- Temperature Conversion Java
- Fahrenheit To Celsius Chart
- Temperature Conversion Chart
Conversion Calculator
Enter your value in the conversion calculator below.
How to convert °C to °F: Enter a value in the °C field and click on the 'Calculate °F' button. Your answer will appear in the °F field.
Conversion Definitions
From Celsius to Fahrenheit: first multiply by 180 100, then add 32. From Fahrenheit to Celsius: first subtract 32, then multiply by 100 180. 180 100 can be simplified to 9 5, and 100 180 can be simplified to 5 9, so this is the easiest way: °C to °F: Divide by 5, then multiply by 9, then add 32. Temperature difference in degrees Fahrenheit calculated by using (3) ΔT(°F) = 1.8 (40 C°) = 72 °F. Temperature Difference Converter. Temperature Difference. Another scale (common in science) is Kelvin, or the Absolute Temperature Scale. On the Kelvin scale the coldest temperature possible, -273 °C, has a value of 0. Distance Converter - Convert Distances! Miles, KM, and more! Length Converter - Convert Lengths! CM, Feet, and more! Percentage Calculator - Work out all the percentages you need! Temperature Converter - Too Hot/ Too Cold? Volume Converter - Find the Volume of a cube! Weight Converter - Convert between weights. Temperature conversions are easy to make through our temp conversion calculator. Let us explain to you a few formulas of conversions that are used by the tool to convert your values. For instance, to convert a temperature value in degrees Fahrenheit to degrees Celsius, you have to subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit value and multiply it by 5/9.
The following is a list of definitions relating to conversions between Celsius and Fahrenheit.
What is degrees Celsius (°C)?
Degrees Celsius is a unit of temperature in the Metric System. The symbol for degrees Celsius is °C. The freezing point is 0°C and the boiling point is 100°C.
What is degrees Fahrenheit (°F)?
Degrees Fahrenheit is a unit of temperature in both US Customary Units as well as the Imperial System. The symbol for degrees Fahrenheit is °F. The freezing point is 32°F and the boiling point is 212°F.
Conversion Formula
Let's take a closer look at the conversion formula so that you can do these conversions yourself with a calculator or with an old-fashioned pencil and paper.
The formula to convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
Conversion Example
Next, let's look at an example showing the work and calculations that are involved in converting from Celsius to Fahrenheit (°C to °F).
Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion Example
Conversion Table
For quick reference purposes, below is a conversion table that you can use to convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion Chart
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|
| -50 °C | -58 °F |
| -45 °C | -49 °F |
| -40 °C | -40 °F |
| -35 °C | -31 °F |
| -30 °C | -22 °F |
| -25 °C | -13 °F |
| -20 °C | -4 °F |
| -15 °C | 5 °F |
| -10 °C | 14 °F |
| -5 °C | 23 °F |
| 0 °C | 32 °F |
| 5 °C | 41 °F |
| 10 °C | 50 °F |
| 15 °C | 59 °F |
| 20 °C | 68 °F |
| 25 °C | 77 °F |
| 30 °C | 86 °F |
| 35 °C | 95 °F |
| 40 °C | 104 °F |
| 45 °C | 113 °F |
| 50 °C | 122 °F |
Related Units
This table provides a summary of the Temperature units within their respective measurement systems.
| Unit | Symbol | Measurement System | Freezing | Boiling | Absolute Zero |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fahrenheit | °F | US Customary Units/Imperial System | 32°F | 212°F | -459.67°F |
| Celsius | °C | Metric System | 0°C | 100°C | -273.15°C |
| kelvin | K | Metric System | 273.15K | 373.15K | 0K |
Find a Conversion
Looking for a conversion? Select a conversion type and the desired units.
Introduction to temperature - including Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin and Rankine definitions - an online temperature converter
Temperature (sometimes called thermodynamic temperature) is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. Temperature is the degree of 'hotness' ( or 'coldness') - a measure of the heat intensity. The most common symbol or abbreviation for temperature is T.
When two objects of different temperatures are in contact - the warmer object becomes colder while the colder object becomes warmer. This means that heat flows from the warmer to the colder object.
Temperature Converter
Convert between °C (Celsius), °F (Fahrenheit),K (Kelvin) and°R (Rankine) with the calculator below:
Temperature Converter - Web App
Add the Temperature Converter Web App to your mobile device or desktop. The App is saved in your browser and works offline automatically after first visit.
Degree Celsius (°C) and Degree Fahrenheit (°F)
A thermometer can help us determine how cold or hot a substance is. Temperature is in most of the world measured and reported in degrees Celsius (°C). In the U.S. it is common to report temperature in degrees Fahrenheit (°F). In the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales the temperatures where ice melts (water freezes) and water boils are used as reference points.
- In the Celsius scale the freezing point of water is defined as 0 °C and the boiling point is defined as 100 °C
- In the Fahrenheit scale the water freezes at 32 °F and boils at 212 °F
In the Celsius scale there are 100 degrees between the freezing point and the boiling point of water compared to 180 degrees in the Fahrenheit scale. This means that 1 °C = 1.8 °F (check the section about temperature differences below).
Temperature Conversion Table
Values can be converted between the two temperature units by using the equations:
T(°F) = 1.8 T(°C) + 32 (1)
T(°C) = (T(°F) - 32)/1.8 (2)
where
T(°C)= temperature (°C )
T(°F)= temperature (°F)
Celsius vs. Fahrenheit
| Temperature | |
|---|---|
| oC | oF |
| -20 | -4 |
| -15 | 5 |
| -10 | 14 |
| -5 | 23 |
| 0 | 32 |
| 5 | 41 |
| 10 | 50 |
| 15 | 59 |
| 20 | 68 |
| 25 | 77 |
| 30 | 86 |
| 35 | 95 |
| 40 | 104 |
| 45 | 113 |
| 50 | 122 |
Example: A patient with SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) has a temperature of 106 °F. What is the temperature in Celsius?
T(°C) = (106 °F - 32)/1.8 = 41.1oC
Temperature Conversion Table - oC vs °F
Temperature Difference - or Temperature Change - degree Celsius versus degree Fahrenheit
Note that for temperature difference (change) - as used in heat loss diagrams
- 1 degree Celsius of temperature differenceequals 1.8 degree Fahrenheit of temperature difference
ΔT(°C) = ΔT(°F) / 1.8(3)
ΔT(°F) = 1.8 ΔT(°C) (4)
where
ΔT(°F) = temperature difference (°F)
ΔT(°C) = temperature difference (°C)
Example: Water is cooled from 100°C to 60°C. What is the temperature difference in °F?
Temperature difference in degrees Celsius:
ΔT(°C) = 100 °C - 60 °C = 40 C°
Note that °C is used for actual temperatures (temperature relative to 273.15 K) and C° is used for temperature differences.
Temperature difference in degrees Fahrenheit calculated by using (1)
100 °C= 1.8 (100 °C) + 32 = 212 °F
60 °C = 1.8 (60 °C) + 32 = 140 °F
ΔT(°F) = 212°F - 140°F = 72 °F
Temperature difference in degrees Fahrenheit calculated by using (3)
ΔT(°F) = 1.8 (40 C°) = 72 °F
Temperature Difference Converter
Temperature Difference
C°°F
Kelvin - K
Another scale (common in science) is Kelvin, or the Absolute Temperature Scale. On the Kelvin scale the coldest temperature possible, -273 °C, has a value of 0 Kelvin (0 K) and is called the absolute zero. Units on the Kelvin scale are called Kelvins (K) and no degree symbol is used.
Because there are no lower temperatures than 0 K - the Kelvin scale does not have negative numbers.
The Kelvin has the same incremental scale as the Celsius scale and one unit Kelvin is equal in size to one unit Celsius:
1 unit Kelvin = 1 unit °C
ΔT(°K) = ΔT(°C) (5)
To calculate a Kelvin temperature, add 273 to the Celsius temperature:
T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15 (6)
Temperature Conversion Equation
Example: What is the normal body temperature of 37 oC in the Kelvin scale?
T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15 = 37°C + 273.15 = 310.15 K
Degree Rankine - R
In the English system the absolute temperature is in degrees Rankine (R), not in Fahrenheit:
T(°R) = 1.8*T(K) (7)
T(°R) = 1.8*(T(°C)+273.15)
T(°R) = T(°F) + 459.67 (8)
ΔT(°R) = ΔT(°F) (9)
Celcius to Fahrenheit Converter (and vice versa)
Temperature Conversion Java
Related Topics
- Basics - The SI-system, unit converters, physical constants, drawing scales and more
- Temperature Measurement - Measurement of temperature - probes, sensors and transmitters
- Thermodynamics - Effects of work, heat and energy on systems
Fahrenheit To Celsius Chart
Related Documents
- Ammonia - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions - Figures and tables showing how the properties of liquid and gaseous ammonia changes along the boiling/condensation curve (temperature and pressure between triple point and critical point conditions). An ammonia phase diagram are included.
- Arithmetic and Logarithmic Mean Temperature Differences in Heat Exchangers - Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference - AMTD - and Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference - LMTD - formulas with examples - Online Mean Temperature Calculator
- Average boiling point from gravity and molecular weight - Formulas and examples of calculation of boiling point of hydrocarbon mixtures from gravity and molecular weight
- Boiling Points for common Liquids and Gases - Boiling temperatures for some common liquids and gases - acetone, butane, propane ..
- Fixed Temperature Points - Temperature points that can be used as a reference for calibration
- Globe Temperature - Resultant or globe temperature
- Ideal Gas Law - The relations between volume, pressure, temperature and quantity of a gas, including definition of density of a gas
- International Standard Atmosphere - International standard atmosphere in elevation -2000 to 30000 metre - pressure, temperature, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity and velocity of sound
- Molecular weight from average boiling point and gravity - Formula and examples of calculation of average molecular weight of hydrocarbon mixtures from gravity and average boiling point, achieved from distillation data.
- Non-ideal gas - Van der Waals equation and constants - Listing of van der Waals constants for more than 200 gases, used to correct for non-ideal behavior of gases caused by intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas particles
- Pt100 - Platinum Resistance Thermometers - Pt100 electrical resistance - ranging -220 to 750 degrees Celsius
- Rankine Efficiency - The efficiency of the Rankine cycle
- RTD - Resistance Temperature Detector - Thermal resistive sensor - a basic introduction
- Survival Time in Cold Water - Time to exhaustion and death in cold water
- Temperature Sensors - Comparing Types - Comparing advantages and disadvantages of thermocouples, RTDs and thermistors temperature sensors
- Thermal Conductivity of Metals, Metallic Elements and Alloys - Thermal conductivity of common metals, metallic elements aand Alloys
- Thermocouples - Thermocouples - types, principles and temperature ranges
- Universal and Individual Gas Constants - The Universal and Individual Gas Constants in fluid mechanics and thermodynamics. Individual gas constant is given for the most common gases.
- Water - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions - Figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, Prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy).
Tag Search
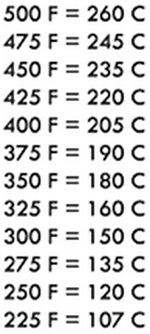
Temperature Conversion Chart
- en: temperature celsius fahrenheit kelvin
- es: temperatura Fahrenheit Centígrados Kelvin
- de: Temperatur Celsius Fahrenheit Kelvin
